What are the 3 types of backup?

The optimal backup strategy varies depending on each organization’s needs. This topic will address the main types of backup methods—full, incremental, and differential—along with their advantages and disadvantages to help you choose what’s best for you and your business.
For example, a small business may choose to back up everything each day, but a large enterprise may choose an incremental or differential backup strategy.
Full Backup
A full backup is when a complete copy of all files and folders is made. This is the most time-consuming backup of all methods to perform and may put a strain on your network if the backup is occurring on the network.
But it’s also the quickest to restore from because all the files you need are contained in the same backup set.
Full backups on a regular schedule require the most storage out of each method.
Advantages
Quick restore time
Disadvantages
Requires the most storage
Uses a lot of network bandwidth
Can be stolen if you don’t encrypt your backups
Because small businesses may not have much data to back up, full backups are probably the best option. It’s easy to maintain and restore them.
However, you should consider encrypting your backups if you plan to use full backups. If an unauthorized user gains access to your backup, they have access to everything if it’s not encrypted. But if your backup is encrypted, they could steal your entire backup drive and still have nothing without your encryption key.

Incremental Backup
This method requires at least one full backup be made, and then afterward only the data that has changed since the last full backup will be backed up again.
Incremental backups take the least space and time to perform than differential and full backups, but it’s the most time-consuming out of all of the methods to restore a full system.
You first have to restore the latest full backup set and then each of the incremental backup sets in order. If one of these backup sets is missing or damaged, then a full restoration is impossible.
Advantages
Takes the least amount of space
Uses relatively little network bandwidth
Disadvantages
Time-consuming restoration
Full restoration impossible if one of the incremental backups is missing or damaged
Businesses who work with large amounts of data will be better served with incremental backups than with full backups alone since incremental backups take up the least space out of each of the three main methods. However, if you cannot go very long without access to your data before losing business or profit, and your recovery time objective (RTO) is very small, consider using a differential backup instead.

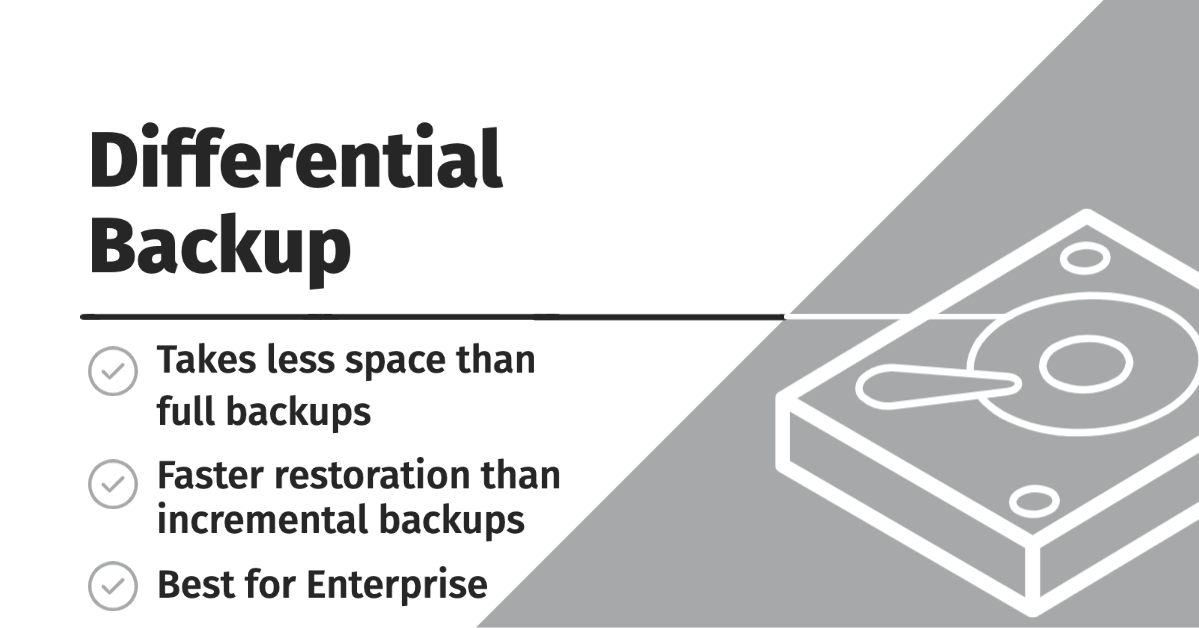
Differential Backup
Differential backups are a compromise between performing regular full backups and regular incremental backups.
Incremental backups require one full backup to be made. Afterward, only the files that have changed since the last full backup are backed up. This means that to restore, you only need the latest full backup set and the latest differential backup set.
There’s no need to restore more than those two backup sets, which saves more time than restoring from an incremental backup, but still takes a bit longer than restoring from a full backup. It also takes up less space than incremental backups, but more space than full backups.
Advantages
Takes less space than full backups
Faster restoration than incremental backups
Disadvantages
Uses much more network bandwidth than incremental backups, but less than full backups
Now that you understand the three main types of backup methods, you should also consider that there are many other types of backup methods that are based upon these.
Some of them include the virtual full backup, near-continuous data protection, reverse incremental backup, and forever incremental backup. One of these may be ideal for your organization.
Craving More?
Sometimes data protection needs more commentary. That’s where our blogs come in. Browse our blog for tips, musings, commentary about industry news, and occassional product news.
Explore Data Protection Topics
SSD vs. HDD
Solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard drives (HDDs) both store computer data and they’re widely used for backups. How data's stored and accessed is the main difference.
Recent Topics
What is a NAS device and how does it work?
Find out what makes a NAS device tick — and if it's the best type of storage solution for you.
What are the 3 types of backup?
There are 3 main types of backup: Full, differential and incremental. See their advantages and disadvantages to help you choose what’s best for you.
Join the ioSafe Community
We’re here to make data protection easy. Join the ioSafe community and we’ll send you:
- Ways to protect your data
- Disaster prep tools
- Data protection best practices